2.6 Using an Ultrasonic Sensor with Smart Pi One¶
This page describes how to use an ultrasonic sensor (e.g., HC-SR04) with the Smart Pi One, providing detailed steps, wiring instructions, and code examples in both Python and C.

Required Materials¶
- Smart Pi One
- Ultrasonic sensor (e.g., HC-SR04)
- Connecting wires
- Breadboard (optional for easier connections)
- 1kΩ and 2kΩ resistors (for voltage divider)
Required Materials¶
- Smart Pi One
- button (with resistor 10kΩ if necessary)
- Connecting wires
- Breadboard (optional for easier connections)
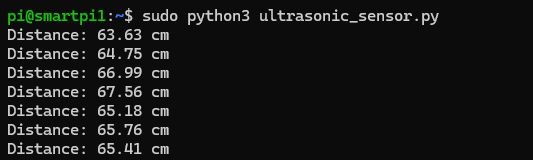
Wiring Diagram¶
Below is a sample wiring diagram for connecting an ultrasonic sensor to the Smart Pi One:
| HC-SR04 Pin | Smart Pi One Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | 5V | Powers the sensor (5V supply) |
| GND | GND | Ground connection |
| TRIG | 7 | Trigger pin connected to GPIO |
| ECHO | 8 | Resistors used to step down voltage from 5V to 3.3V to protect the GPIO pin - 1kΩ + 2kΩ (Voltage Divider) |
Important Note:¶
- ECHO pin (GPIO8) requires a voltage divider to step down the 5V output signal from the sensor to 3.3V, which is safe for the GPIO pin on the Smart Pi One.
- Connect a 1kΩ resistor between the ECHO pin and the GPIO pin.
- Connect a 2kΩ resistor between the GPIO pin and GND to complete the voltage divider.
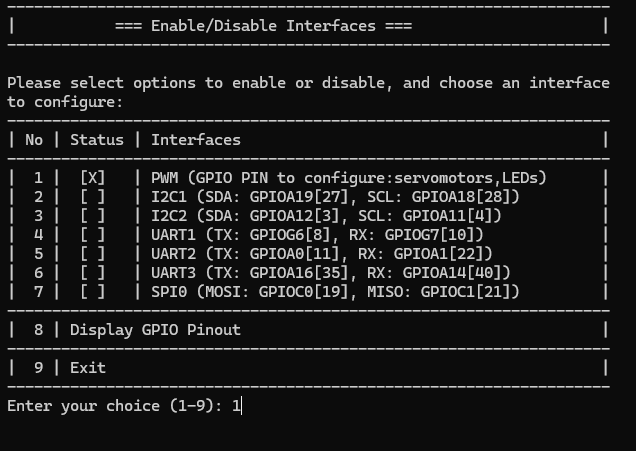
Prerequisites: Configuration of smartpi-gpio¶
To install SmartPi-GPIO on your Smart Pi One, follow these steps:
- Update system:
sudo apt update
sudo apt-get install -y python3-dev python3-pip libjpeg-dev zlib1g-dev libtiff-dev
sudo mv /usr/lib/python3.11/EXTERNALLY-MANAGED /usr/lib/python3.11/EXTERNALLY-MANAGED.old
- Clone the repository:
- Install the library:
- Activate GPIO interfaces:
Using Python¶
Prerequisites: Configuration of smartpi-gpio¶
- Open a terminal on your Smart Pi One.
- Create a new Python file using
nano:
- Copy and paste the following Python code into the file:
import time
from smartpi_gpio.gpio import GPIO
# Initialize GPIO
gpio = GPIO()
TRIG = 7
ECHO = 8
# Set GPIO pins
gpio.setup(TRIG, gpio.OUT)
gpio.setup(ECHO, gpio.IN)
try:
while True:
# Send a pulse
gpio.output(TRIG, gpio.HIGH)
time.sleep(0.00001) # 10 microseconds
gpio.output(TRIG, gpio.LOW)
# Wait for the echo to start
while gpio.input(ECHO) == gpio.LOW:
start_time = time.time()
# Wait for the echo to stop
while gpio.input(ECHO) == gpio.HIGH:
end_time = time.time()
# Calculate distance
duration = end_time - start_time
distance = (duration * 34300) / 2 # Speed of sound is 34300 cm/s
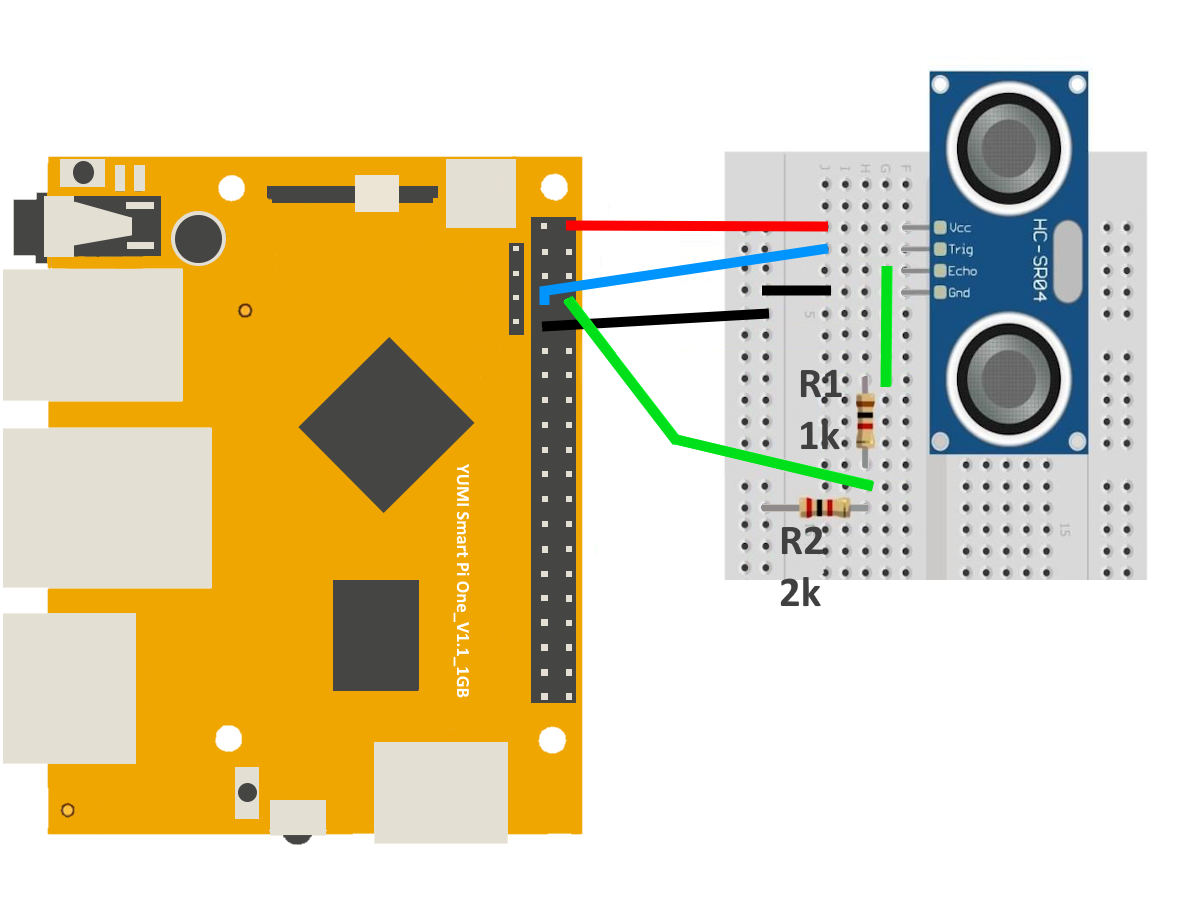
print(f"Distance: {distance:.2f} cm")
time.sleep(1) # Wait 1 second before next measurement
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
finally:
gpio.cleanup() # Clean up GPIO
- Save the file by pressing
CTRL + X, thenY, and finallyEnter.
Running the Python Script¶
To run the Python script, use the following command: